How Is Endometriosis Diagnosed: A Comprehensive Guide to Accurate Detection and Treatment
Endometriosis is a complex and often misunderstood condition affecting millions of women worldwide. Proper diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and improved quality of life. In this article, we delve deeply into how is endometriosis diagnosed, exploring the symptoms, diagnostic procedures, advances in medical technology, and specialized care options available through top obstetricians & gynecologists, such as those at drseckin.com.
Understanding Endometriosis and Its Impact on Women's Health
Endometriosis is a chronic condition where tissue similar to the endometrial lining of the uterus grows outside the uterine cavity. This misplaced tissue primarily affects the pelvic organs but can sometimes involve areas beyond the pelvis. The condition causes severe pain, fertility issues, and a range of other symptoms that can significantly disrupt daily life.
The challenge with endometriosis lies in its elusive diagnosis. Symptoms often overlap with other gynecological issues, and definitive diagnosis requires a combination of clinical assessment and sophisticated diagnostic tools. Gaining clarity on how is endometriosis diagnosed is essential for timely and effective treatment strategies.
Common Symptoms Indicating Need for Endometriosis Diagnosis
- Pelvic Pain: Chronic pain before and during menstruation, which may intensify over time.
- Painful Menstruation (Dysmenorrhea): Severe menstrual cramps that interfere with daily activities.
- Pain During Intercourse: Deep pain or discomfort during or after sex.
- Infertility: Trouble conceiving despite regular unprotected intercourse.
- Gastrointestinal Symptoms: Bloating, diarrhea, constipation, or nausea, especially during menstruation.
- Other Symptoms: Fatigue, urinary issues, or lower back pain.
These symptoms can often be mistaken for other conditions, which makes an accurate diagnosis even more vital for proper management.
Diagnostic Approaches to How Is Endometriosis Diagnosed
1. Clinical Evaluation and Detailed Medical History
The journey toward diagnosis begins with a thorough medical history review and physical examination. Your healthcare provider, such as a specialist at drseckin.com, will inquire about your symptoms, their severity, duration, and impact on daily activities. A comprehensive pelvic exam may reveal tender regions, nodules, or adhesions associated with endometriosis.
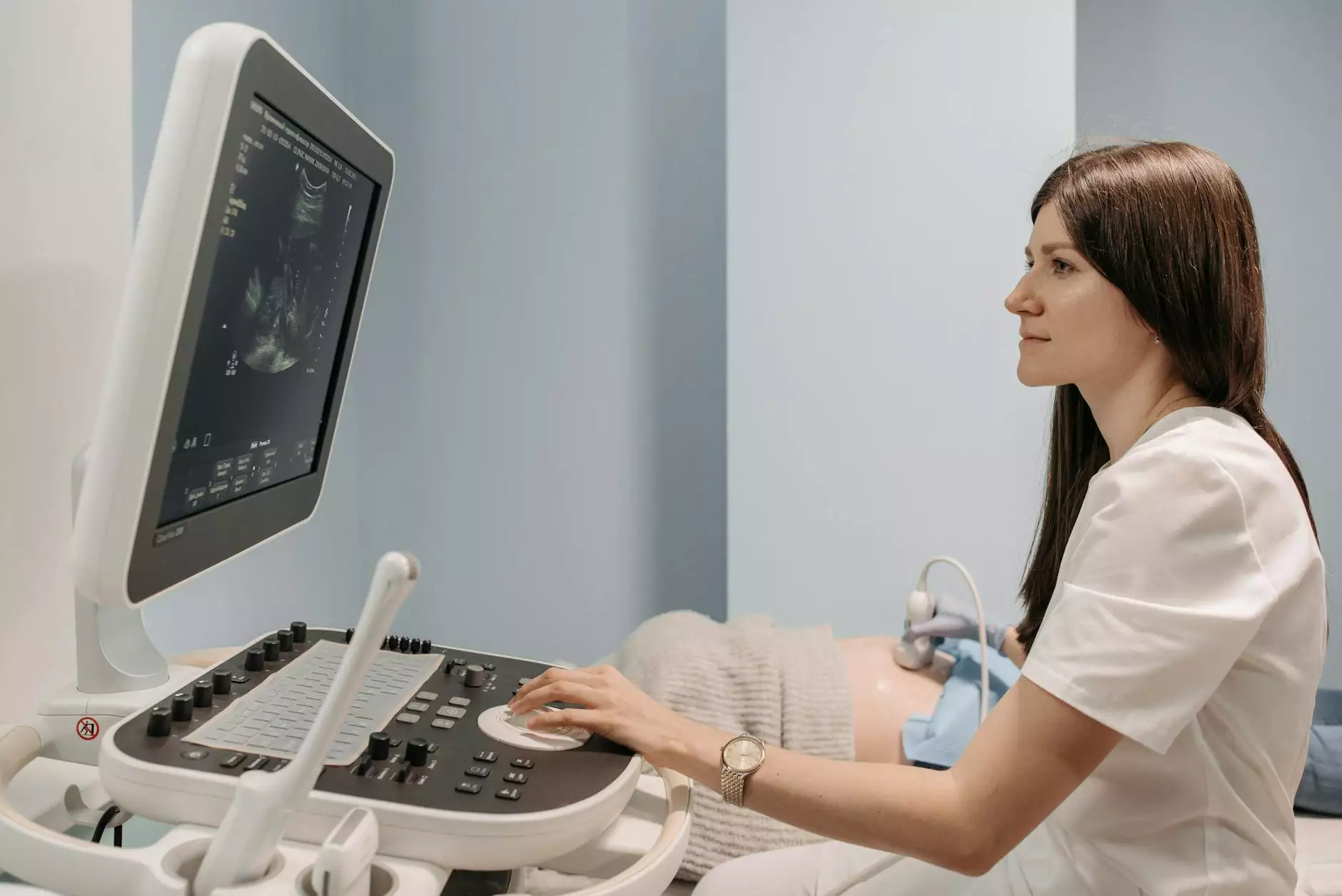
2. Imaging Tests for Initial Assessment
While imaging cannot definitively diagnose endometriosis, it plays a pivotal role in ruling out other conditions and identifying certain features of the disease.
- Ultrasound: Transvaginal ultrasound is the most common imaging modality to detect ovarian endometriomas (benign cysts formed by endometrial tissue) and other pelvic abnormalities.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Provides detailed images of pelvic organs and can help identify deep infiltrating endometriosis (DIE), especially in complex cases or when surgical planning is required.
These imaging techniques are useful tools but have limitations in detecting superficial endometrial implants.
3. The Role of Laparoscopy in Accurate Diagnosis
Despite advances in imaging, how is endometriosis diagnosed with absolute certainty is primarily through a minimally invasive surgical procedure known as laparoscopy.
Laparoscopy is considered the gold standard for diagnosing endometriosis because it allows direct visualization of endometrial lesions and the opportunity to perform simultaneous treatment. During the procedure, the surgeon inserts a thin camera through a small incision in the abdomen, meticulously inspecting pelvic and abdominal organs for characteristic lesions, adhesions, or nodules.
Biopsies can be obtained during laparoscopy to confirm the diagnosis histopathologically, ensuring that the visible lesions are indeed endometrial tissue and not other pathologies.
Advanced Diagnostic Techniques and Innovations in Endometriosis Detection
4. Biomarker Testing: The Future of Non-Invasive Diagnosis
Emerging research focuses on identifying specific biomarkers present in blood or other body fluids that could facilitate non-invasive diagnosis of endometriosis. These biomarkers may include certain proteins, microRNAs, or inflammatory markers that reflect the presence of endometrial tissue outside the uterus.
While these tests are still under development, they represent a promising avenue to reduce the reliance on invasive procedures like laparoscopy in the future.
5. Imaging Enhancements with 3D and 4D Modalities
Technological innovations in imaging, such as 3D ultrasound and 4D MRI, offer enhanced visualization and more precise mapping of endometrial lesions. These tools could improve detection rates, especially for deep infiltrating endometriosis, facilitating surgical planning and personalized treatment approaches.
Why Early and Accurate Diagnosis Matters
Timely identification of endometriosis can significantly improve patient outcomes. Delayed diagnosis is common, often spanning several years, which can lead to worsening pain, increased chances of fertility problems, and psychological distress.
By understanding how is endometriosis diagnosed accurately, healthcare providers can initiate appropriate treatments sooner, including medical therapy, surgical intervention, or a combination of both, tailored to the individual's severity and specific condition.
Effective Treatment Options Post-Diagnosis
Once diagnosed, managing endometriosis involves a multidisciplinary approach that includes:
- Medical Therapy: Hormonal treatments such as birth control pills, GnRH agonists, and progestins to suppress endometrial tissue growth and reduce symptoms.
- Surgical Intervention: Excision or ablation of endometrial lesions, especially in severe cases or when attempting to restore fertility.
- Fertility Treatments: For women facing infertility, options like assisted reproductive technologies (ART) may be recommended.
- Supportive Care: Pain management, physical therapy, and counseling for emotional support and quality of life improvements.
Choosing the Right Specialist for Diagnosis and Treatment
Finding experienced obstetricians & gynecologists, such as those at drseckin.com, is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management of endometriosis. These specialists possess advanced training in minimally invasive gynecologic surgery and are familiar with the latest diagnostic protocols.
Leading specialists can provide comprehensive care, guiding you through your diagnosis journey with personalized treatment plans designed to address your specific symptoms and reproductive goals.
Conclusion: Navigating the Path to Diagnosis and Better Health
Understanding how is endometriosis diagnosed is essential for women experiencing symptoms. Although challenges exist, modern diagnostic methods—ranging from detailed clinical evaluations and imaging to definitive laparoscopic procedures—enable accurate detection. With ongoing advances in biomarker research and imaging technology, the future holds promise for non-invasive and earlier diagnosis.
If you suspect you have endometriosis or are experiencing related symptoms, consulting experienced healthcare providers at specialized clinics like drseckin.com ensures the best possible care. Early diagnosis and tailored treatment are key to managing symptoms effectively, restoring fertility, and improving overall quality of life.
Remember, proactive health management and seeking expert advice are your best tools in the journey toward understanding and overcoming endometriosis.
how is endometriosis diagnoses








